Crypto arbitrage, at its core, is a trading strategy that capitalizes on price discrepancies of a digital asset across multiple markets or exchanges. It’s a concept that has been employed in traditional financial markets for decades, but with the advent of cryptocurrencies, it has gained renewed interest and potential for profit.
What is Crypto Arbitrage?
Crypto arbitrage is the process of buying a cryptocurrency on one exchange where the price is lower and then selling it almost simultaneously on another exchange where the price is higher. The difference in price between the two exchanges is the profit. This might sound simple, but in the fast-paced world of cryptocurrencies, even seconds can make a difference in profitability.
Basic Example of Crypto Arbitrage:
- Exchange A:
- Cryptocurrency: Bitcoin (BTC)
- Price: $45,000
- Exchange B:
- Cryptocurrency: Bitcoin (BTC)
- Price: $45,200
In the list above, if a trader buys 1 Bitcoin on Exchange A for $45,000 and sells it on Exchange B for $45,200, they would make a profit of $200 (excluding any transaction fees).
Historical Relevance in Traditional Financial Markets
Long before the emergence of cryptocurrencies, arbitrage has been a staple in traditional financial markets. Stocks, commodities, and currencies often have slight price discrepancies across different exchanges or platforms. Traders have been exploiting these discrepancies for years to secure risk-free profits.
However, the crypto market offers unique advantages for arbitrage. Given its decentralized nature, the crypto market operates 24/7, providing continuous opportunities for traders. Moreover, the market is still relatively young, leading to more significant price discrepancies than in more mature traditional markets.
Why is Crypto Arbitrage Popular?
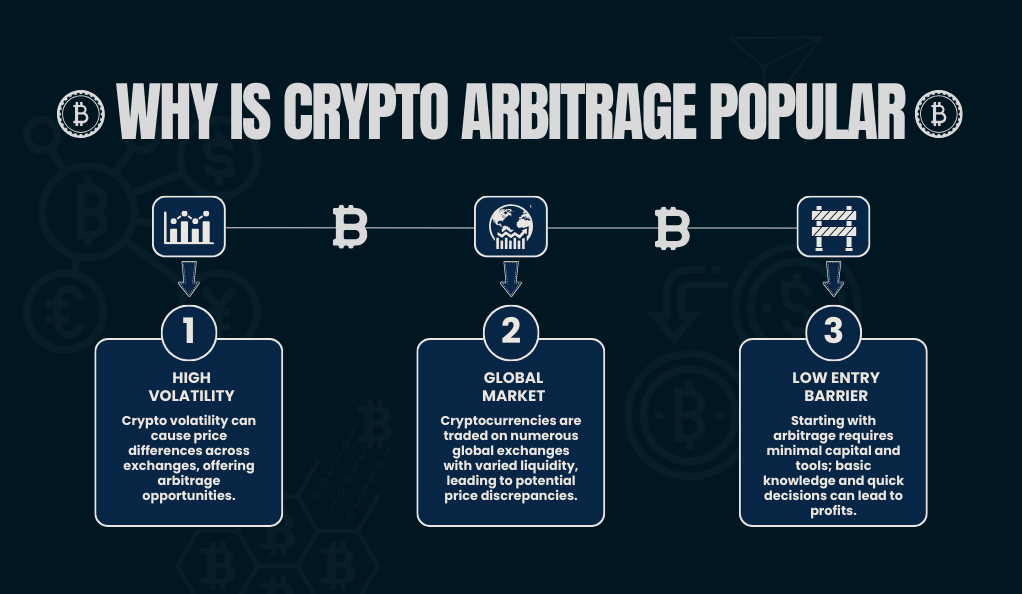
There are a few reasons for the popularity of crypto arbitrage:
- High Volatility: Cryptocurrencies are known for their price volatility. This volatility can lead to significant price differences across exchanges, creating ample opportunities for arbitrage.
- Global Market: Cryptocurrencies are traded globally, meaning there are hundreds of exchanges operating in different time zones and with varying levels of liquidity. This global nature further increases the chances of price discrepancies.
- Low Entry Barrier: Unlike some advanced trading strategies, getting started with arbitrage doesn’t require significant capital or sophisticated tools. With basic knowledge and quick decision-making, anyone can attempt to profit from arbitrage opportunities.
Why X11-based Cryptocurrencies?
The world of cryptocurrencies is vast, with over thousands of different coins and tokens, each built on various algorithms and serving diverse purposes. Among these, the X11 algorithm stands out for its unique features and the opportunities it presents for traders, especially in the realm of arbitrage. But what exactly is X11, and why should arbitrage traders pay attention to it?
Understanding the X11 Algorithm
The X11 algorithm is a proof-of-work (PoW) hashing algorithm that uses a sequence of eleven scientific hashing algorithms for the proof-of-work. This makes it one of the most complex cryptographic algorithms employed for mining and blockchain consensus. Some of the popular cryptocurrencies that use the X11 algorithm include Dash, Pura, and CannabisCoin.
| Cryptocurrency | Market Cap (as of writing) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Dash | $x billion | InstantSend, PrivateSend, decentralized governance |
| Pura | $x million | Masternodes, swift transactions, eco-friendly |
| CannabisCoin | $x million | Designed for cannabis dispensaries |
Advantages of X11-based Cryptocurrencies
One of the defining characteristics of the X11 algorithm is its energy efficiency, setting it apart from other Proof-of-Work (PoW) algorithms. This efficiency translates to X11-based cryptocurrency mining consuming less power, offering both an environmentally friendly and cost-effective advantage for miners. Furthermore, the incorporation of eleven hashing functions bolsters the security of X11, fortifying it against potential vulnerabilities and threats. In terms of price dynamics, while volatility is inherent to all cryptocurrencies, those based on the X11 algorithm tend to exhibit a marginally more stable price trajectory. Such stability can be particularly beneficial for arbitrage, as it fosters a more predictable landscape for identifying price discrepancies.
Arbitrage Opportunities with X11-based Cryptocurrencies
Given the unique features of X11-based cryptocurrencies, they present specific arbitrage opportunities:
- Diverse Exchange Listings: X11 coins, especially popular ones like Dash, are listed on multiple exchanges, both big and small. This diversity can lead to price discrepancies, ripe for arbitrage.
- Liquidity Variations: Not all exchanges have the same liquidity for X11 coins. Some might have high trading volumes, leading to more stable prices, while others might experience sudden price spikes or drops.
- Regional Price Differences: Cryptocurrencies, including those based on X11, can have different prices based on regional demand and supply. For instance, Dash might be priced differently on an Asian exchange compared to a European one due to variations in adoption, regulations, and market sentiment.
Volatility in the Crypto Market
One of the defining characteristics of the cryptocurrency market is its volatility. Prices can soar or plummet within minutes, and this dynamic nature of the market is both a boon and a bane for traders. For arbitrage traders, volatility can present numerous opportunities, but it also comes with its set of challenges.
Understanding the Causes of Volatility
Several factors contribute to the high volatility observed in the crypto market:
- Market Maturity: Compared to traditional financial markets, the cryptocurrency market is relatively young. Established just over a decade ago, it’s still in its nascent stages, leading to price instability.
- Speculative Nature: A significant portion of crypto trading is driven by speculation. Traders often buy assets hoping their prices will rise, rather than based on their fundamental value. This speculative trading can lead to rapid price fluctuations.
- Regulatory News: Announcements related to cryptocurrency regulations, whether positive or negative, can have a substantial impact on prices. For instance, news about a country banning crypto trading can lead to a sharp decline in prices.
- Technological Developments: Updates or vulnerabilities in blockchain technology can influence prices. A security breach in a popular cryptocurrency or the launch of a new feature can lead to price volatility.
- Supply and Demand Dynamics: The basic economic principle of supply and demand plays a crucial role. Limited supply of certain cryptocurrencies combined with high demand can lead to price surges.
Major Crypto Price Movements and Their Causes:
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Cryptocurrency: Bitcoin (BTC)
- Price Movement: +15%
- Probable Cause: Positive regulatory news in Country X
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Cryptocurrency: Ethereum (ETH)
- Price Movement: -10%
- Probable Cause: Security vulnerability discovered
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Cryptocurrency: Dash (X11)
- Price Movement: +8%
- Probable Cause: Launch of a new feature
Volatility and Arbitrage Opportunities
For arbitrage traders, the volatility of the crypto market is akin to a goldmine. This is primarily because rapid price movements increase the likelihood of spotting price discrepancies across exchanges. For example, due to sudden market shifts, Bitcoin might be priced at $45,000 on one exchange and $45,500 on another. Additionally, the essence of arbitrage trading is to make quick trades, and the fast-paced nature of the crypto market enables traders to seize opportunities and secure profits in mere minutes or even seconds.
However, this volatility isn’t without its challenges. An arbitrage opportunity that’s present one moment might vanish the next due to swift price convergence across exchanges. Moreover, the heightened volatility implies that prices can swiftly move against a trader’s position. If trades aren’t executed in a timely manner, what initially appeared as a lucrative arbitrage chance could lead to losses.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Exchanges
The cryptocurrency market operates on various platforms, primarily categorized into centralized and decentralized exchanges. Both types of exchanges play a crucial role in the crypto ecosystem, and understanding their differences is vital for arbitrage traders.
Centralized Exchanges (CEX)
Centralized exchanges are platforms operated by centralized entities or companies. They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, much like traditional stock exchanges.
Key Features of Centralized Exchanges:
- Controlled Environment: CEXs are managed by a single entity, ensuring a controlled trading environment with set rules and regulations.
- High Liquidity: Due to their popularity and ease of use, CEXs often have high trading volumes, leading to better liquidity.
- Advanced Trading Tools: Many CEXs offer advanced trading tools, charts, and features, catering to both novice and professional traders.
- Custodial Wallets: These exchanges hold users’ funds in custodial wallets, which means the exchange has control over the private keys.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
Decentralized exchanges operate without a central authority. They facilitate peer-to-peer trading, and transactions are executed using smart contracts on a blockchain.
Key Features of Decentralized Exchanges:
- No Central Authority: DEXs operate autonomously without any central governing body, ensuring true decentralization.
- Non-custodial: Users retain control of their private keys and funds, reducing the risk of exchange hacks.
- Privacy and Anonymity: Most DEXs don’t require users to undergo identity verification, ensuring higher privacy.
- Global Accessibility: Without centralized control, DEXs are accessible to anyone, anywhere, without restrictions.
| Feature | Centralized Exchange | Decentralized Exchange |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Central entity | None (P2P) |
| Liquidity | High | Varies |
| Trading Tools | Advanced | Basic |
| Custody of Funds | Exchange | User |
| Identity Verification | Often required | Rarely required |
Implications for Arbitrage Trading
- Price Discrepancies: Due to the inherent differences in operation, liquidity, and user base, price discrepancies between CEXs and DEXs can be common, offering arbitrage opportunities.
- Speed of Transactions: Centralized exchanges often offer faster trade execution due to their infrastructure. In contrast, DEXs rely on blockchain confirmations, which might be slower.
- Fees: CEXs typically have a structured fee system, while DEXs might have variable fees based on network congestion.
- Risk Profile: Trading on CEXs comes with the risk of exchange hacks, while DEXs eliminate this risk but introduce smart contract vulnerabilities.
Types of Crypto Arbitrage Strategies
In the realm of crypto arbitrage, there isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach. Different strategies cater to various market conditions, risk appetites, and trader expertise. Let’s delve into the most popular crypto arbitrage strategies and understand their intricacies.
Cross-exchange Arbitrage
This is the most straightforward form of arbitrage and involves buying a cryptocurrency on one exchange where the price is lower and selling it on another where the price is higher.
Example: If Bitcoin is priced at $45,000 on Exchange A and $45,500 on Exchange B, a trader can buy on A and sell on B, pocketing the $500 difference (minus fees).
Spatial Arbitrage
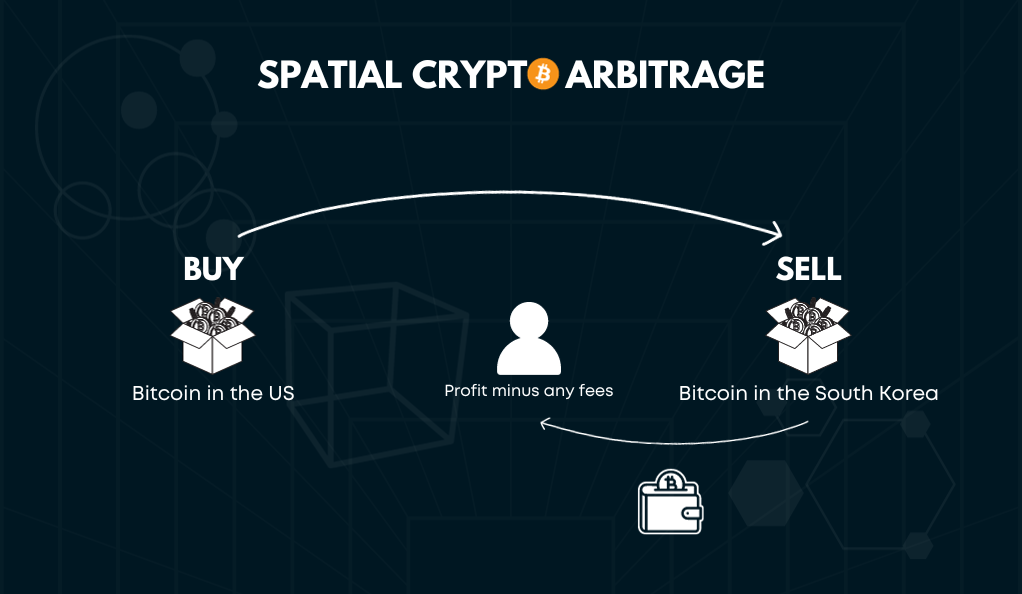
Spatial arbitrage involves exploiting price differences of a cryptocurrency in different geographical locations. Due to regional demand, regulations, or liquidity issues, a cryptocurrency might be priced differently in two countries.
Example: Bitcoin might be priced higher in South Korea compared to the US due to higher demand. A trader can buy Bitcoin in the US and sell it in South Korea, benefiting from the price difference.
Triangular Arbitrage
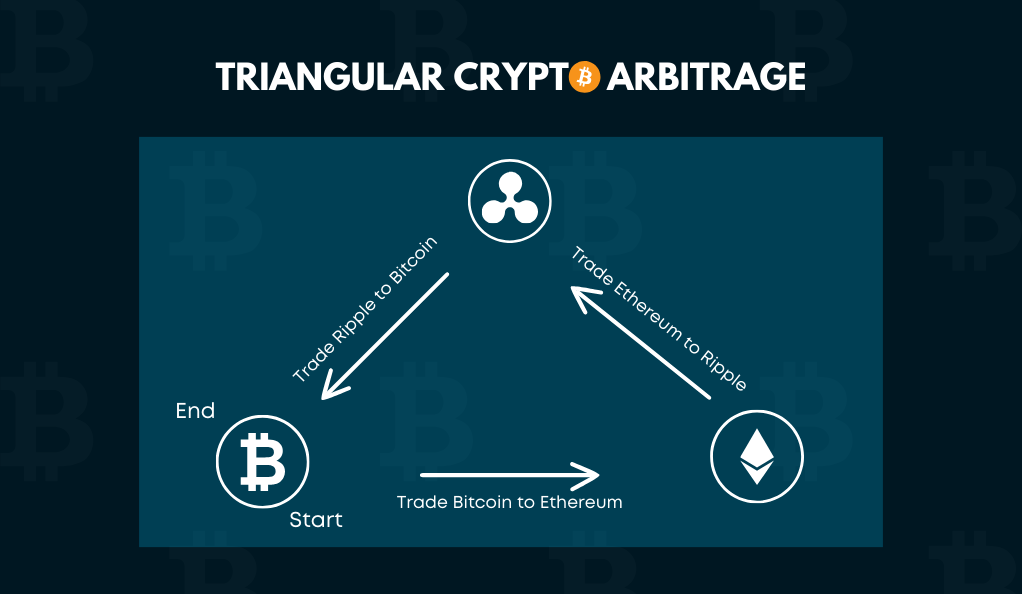
This strategy involves three trades and three different cryptocurrencies. The idea is to exploit discrepancies in prices between these cryptocurrencies on a single exchange.
Example: A trader starts with Bitcoin, trades it for Ethereum, then trades Ethereum for Ripple, and finally trades Ripple back to Bitcoin. If done correctly, the trader ends up with more Bitcoin than they started with.
Decentralized Arbitrage
This strategy focuses on exploiting price differences between centralized and decentralized exchanges. Given the different operational mechanisms of CEXs and DEXs, price discrepancies can arise.
Example: Ethereum might be priced lower on a DEX compared to a CEX. A trader can buy Ethereum on the DEX and sell it on the CEX for a profit.
Statistical Arbitrage
This is a more advanced form of arbitrage that involves mathematical models and algorithms. Traders analyze historical price data to predict future price movements and make trades based on these predictions.
Example: If historical data shows that whenever the price difference between Bitcoin and Ethereum reaches a certain threshold, it narrows down within a specific timeframe, traders can use this information to make arbitrage trades.
Risks and Challenges in Crypto Arbitrage
While crypto arbitrage presents numerous opportunities for profit, it’s not without its risks and challenges. Understanding these potential pitfalls is crucial for traders to navigate the crypto landscape effectively and protect their investments.
Transaction Fees
Every trade on an exchange comes with a fee. When executing arbitrage strategies, especially those involving multiple trades, these fees can quickly add up and eat into potential profits.
Example: If the price difference between Bitcoin on two exchanges is $100, but the combined fees for buying and selling amount to $105, the trader would incur a net loss.
Timing and Market Dynamics
The crypto market is incredibly fast-paced. An arbitrage opportunity that exists one moment might disappear the next. Delays in executing trades, transferring funds between exchanges, or blockchain confirmations can result in missed opportunities or losses.
Exchange Liquidity
Not all exchanges have the same liquidity levels. Trying to sell a large amount of a cryptocurrency on an exchange with low liquidity can lead to “slippage,” where the price drops due to the large sell order, reducing potential profits.
Exchange Hacks and Security Concerns
Centralized exchanges, where the majority of trading volume occurs, are targets for hackers. Funds stored on an exchange can be at risk. While decentralized exchanges reduce this risk, they come with their own set of vulnerabilities, like smart contract bugs.
Regulatory Risks
The regulatory environment for cryptocurrencies is still evolving. Sudden regulatory changes or interventions can lead to rapid market shifts, impacting arbitrage opportunities. Moreover, some arbitrage strategies, like spatial arbitrage, can be affected by country-specific regulations.
Wallet and Transfer Delays
Transferring funds between wallets or exchanges isn’t always instantaneous. Network congestion, especially on popular blockchains like Ethereum, can lead to delays. These delays can be detrimental for arbitrage traders, especially when prices are volatile.
Impermanent Loss (For Decentralized Finance Arbitrage)
In the realm of decentralized finance (DeFi), liquidity providers can face impermanent loss when providing assets to liquidity pools. This loss occurs when the price of the provided assets changes compared to when they were deposited.
Getting Started with Arbitrage Trading
Embarking on the journey of crypto arbitrage trading can seem daunting, especially given the rapid pace of the crypto market and the myriad of strategies available. However, with the right tools, knowledge, and mindset, traders can navigate this landscape effectively. Here’s a step-by-step guide to getting started with arbitrage trading.
Research and Education
Before diving into arbitrage trading, it’s essential to have a solid understanding of the crypto market, the mechanics of different exchanges, and the various arbitrage strategies.
- Resources: Books, online courses, webinars, and forums can provide valuable insights.
- Stay Updated: The crypto landscape is ever-evolving. Regularly following crypto news sites and forums can help traders stay abreast of market developments.
Choose the Right Exchanges
Given the plethora of exchanges available, selecting the right ones is crucial. Factors to consider include:
- Liquidity: Higher liquidity often means more stable prices and easier trade execution.
- Fees: Lower trading fees can significantly impact profitability.
- Security: Opt for exchanges with robust security measures to protect your assets.
Equip Yourself with Tools
Several tools and platforms can aid in spotting arbitrage opportunities:
- Arbitrage Bots: These are automated tools that can identify and even execute arbitrage trades on behalf of the trader.
- Price Trackers: Platforms that provide real-time price data across various exchanges.
- Portfolio Trackers: Tools that help traders monitor their holdings across different exchanges.
Start with a Test Run
Before committing significant capital, it’s wise to start with small trades to understand the dynamics of arbitrage trading.
- Paper Trading: Some platforms offer simulated trading environments where traders can practice without risking real money.
- Small Trades: Begin with smaller amounts to understand the process and refine your strategy.
Monitor and Adjust
The crypto market is dynamic, and what works today might not work tomorrow. Regularly reviewing and adjusting your strategies is essential.
- Track Performance: Maintain a trading journal to review your successes and areas of improvement.
- Stay Informed: Market dynamics, regulations, and technological advancements can impact arbitrage opportunities. Staying informed helps traders adapt.
Manage Risks
As with any trading strategy, managing risks is paramount in arbitrage trading.
- Diversify: Don’t put all your capital into one strategy or market.
- Set Limits: Determine in advance the maximum amount you’re willing to risk on a trade.
- Stay Updated on Security: Regularly update software, use hardware wallets, and enable two-factor authentication to protect your assets.
Conclusion
The realm of crypto arbitrage, with its blend of opportunities and challenges, offers traders a dynamic landscape to navigate. From the volatility of the crypto market to the myriad of strategies available, success hinges on agility, continuous learning, and the right tools. While the promise of quick profits is alluring, it’s essential to approach crypto arbitrage with analytical prowess, strategic planning, and an understanding of the associated risks.
As the crypto world continues to evolve, so too will the nuances of arbitrage trading, especially with emerging technologies and changing regulations. Staying updated, adaptable, and maintaining a keen sense of curiosity will be paramount for traders aiming to harness the full potential of this exciting trading strategy.
At axerunners.com, our goal is to furnish well-rounded and trustworthy information regarding cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and stocks. Nonetheless, we avoid providing financial advice and instead encourage users to conduct their own research and meticulous verification.
Read More











