Decentralized Finance, commonly known as DeFi, represents a transformative shift in the world of finance. It’s a term that has rapidly gained traction in the cryptocurrency and blockchain space, and for a good reason. But what exactly is DeFi, and why is it so significant?
What is DeFi?
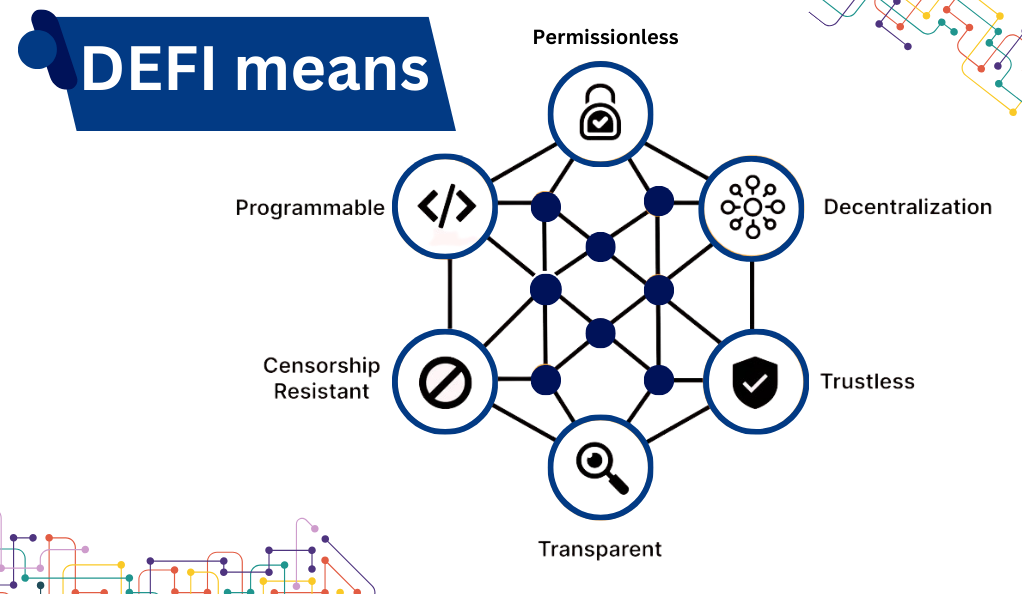
At its core, DeFi refers to a system where financial products become available on a public decentralized blockchain network, making them open to anyone to use, rather than going through middlemen like banks or brokers. These decentralized platforms run on smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts where the terms of agreement or conditions are written into lines of code.
| Criteria | Traditional Finance | DeFi |
|---|---|---|
| Intermediaries | Banks, Brokers | None (or automated protocols) |
| Accessibility | Often restricted | Open to anyone with internet |
| Transparency | Limited | Fully transparent |
| Control | Centralized institutions | Users and smart contracts |
Why is DeFi Significant?
- Democratization of Finance: DeFi has the potential to democratize access to financial services. In a world where nearly 1.7 billion adults remain unbanked, DeFi opens doors to financial tools and services, from simple savings and lending platforms to complex trading and insurance products.
- Transparency and Security: Built on blockchain technology, all transactions on DeFi platforms are transparent and can be audited by anyone. This transparency reduces the chances of fraud and malpractice. Additionally, the decentralized nature of these platforms reduces single points of failure, making them more resilient to attacks.
- Innovation and Flexibility: The open-source nature of DeFi projects encourages innovation. Developers from around the world can collaborate, iterate, and build upon existing protocols, leading to rapid advancements and the creation of diverse financial products.
- Cost Efficiency: Without intermediaries taking a cut, transactions on DeFi platforms can be more cost-effective. Users often experience lower fees and better interest rates compared to traditional financial systems.
The Evolution of DeFi
The journey of Decentralized Finance is a testament to the power of innovation and the relentless pursuit of decentralization in the financial sector. To truly appreciate the current state of DeFi, it’s essential to trace its evolution.
The Genesis: Bitcoin and the Idea of Decentralized Money
The roots of DeFi can be traced back to the inception of Bitcoin in 2009. While Bitcoin itself isn’t a DeFi platform, it introduced the world to the revolutionary idea of decentralized money – a currency without a central authority. This was the first step towards a decentralized financial ecosystem.
Ethereum and the Advent of Smart Contracts
While Bitcoin showcased the potential of decentralized money, Ethereum, launched in 2015, took it a step further. Ethereum introduced the concept of “smart contracts,” which are programmable contracts that automatically execute when certain conditions are met. This innovation laid the foundation for the DeFi platforms we see today.
The Blossoming of DeFi Platforms
Post-2017, the DeFi ecosystem began to flourish. With the infrastructure provided by Ethereum, developers started creating decentralized applications (dApps) that mimicked traditional financial instruments:
- Lending and Borrowing: Platforms like Compound and Aave allowed users to lend and borrow assets without intermediaries, using smart contracts to automate the process.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Unlike traditional exchanges, DEXs like Uniswap and Sushiswap operate without a central authority, allowing peer-to-peer trades.
- Stablecoins: To address the volatility of cryptocurrencies, stablecoins like USDC and DAI were introduced. These are pegged to stable assets like the US dollar and are crucial for many DeFi applications.
Challenges and Setbacks
Like any nascent industry, DeFi faced its share of challenges. The ecosystem saw hacks, with millions lost due to vulnerabilities in smart contracts. There were also “rug pulls” where malicious actors abandoned projects after raising funds. These incidents highlighted the importance of security and due diligence in the DeFi space.
The Current Landscape and Beyond
Today, DeFi has grown beyond Ethereum, with other blockchains like Binance Smart Chain, Polkadot, and Solana offering their own DeFi solutions. The total value locked (TVL) in DeFi platforms has crossed billions, indicating a strong trust and interest in decentralized financial solutions.
Understanding Tokenomics in DeFi
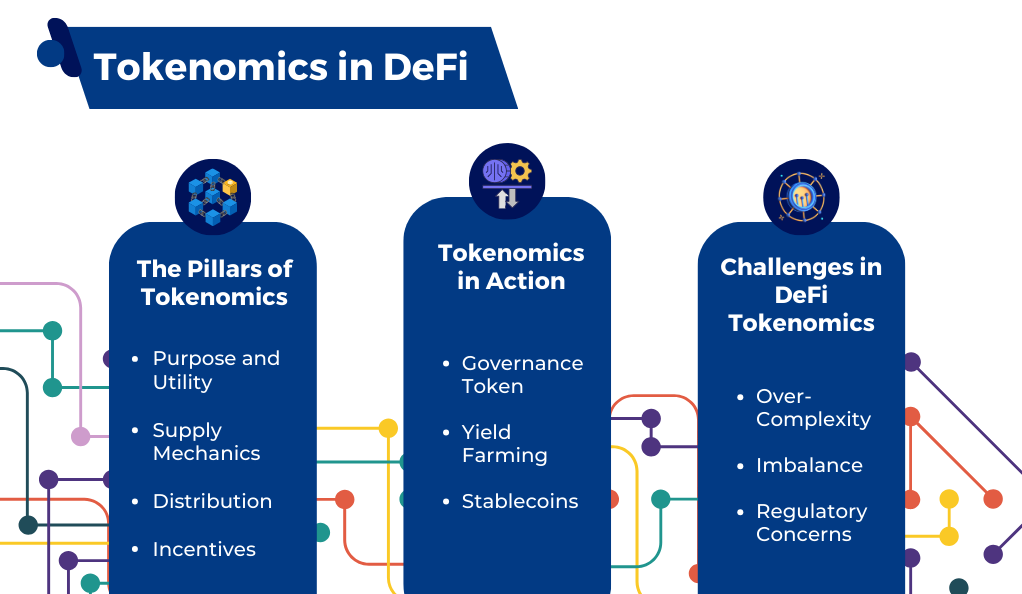
Tokenomics, a fusion of ‘token’ and ‘economics’, is the study of the economic systems surrounding blockchain tokens. In the DeFi space, understanding tokenomics is crucial as it dictates the value, utility, and potential success of a project. Let’s delve deeper into the intricacies of tokenomics within DeFi.
The Pillars of Tokenomics
- Purpose and Utility: Every token must have a clear purpose. Whether it’s governance, staking, rewards, or fees, the utility of a token determines its demand and value in the ecosystem.
- Supply Mechanics: This encompasses the total supply, issuance rate, and any potential burns or inflationary measures. A well-balanced supply mechanic ensures scarcity and demand without causing excessive inflation.
- Distribution: How tokens are distributed can impact the decentralization and security of the network. Fair distribution methods prevent centralization and promote wider adoption.
- Incentives: Tokenomics should incentivize good behavior (like staking or providing liquidity) and penalize bad behavior (like early unstaking or malicious activities).
Tokenomics in Action: DeFi Examples
- Governance Tokens: Platforms like Compound and MakerDAO have governance tokens (COMP and MKR respectively) that allow holders to vote on protocol changes. This not only decentralizes decision-making but also gives token holders a stake in the platform’s future.
- Yield Farming: Projects like Yearn.finance introduced the concept of yield farming, where users earn tokens as rewards for providing liquidity or participating in a protocol. This incentivizes user participation and boosts platform adoption.
- Stablecoins: The tokenomics of stablecoins like DAI revolves around collateralization. Users lock up assets as collateral to mint stablecoins, ensuring that the stablecoin maintains its peg.
Challenges in DeFi Tokenomics
- Over-Complexity: Some projects introduce overly complex tokenomics, which can deter users and lead to unforeseen consequences.
- Imbalance: A misalignment of incentives can lead to centralization or exploitation. For instance, excessive rewards for early adopters can lead to “pump and dump” scenarios.
- Regulatory Concerns: As DeFi grows, regulatory bodies are taking note. The design of tokenomics must consider potential regulatory implications, especially concerning securities laws.
X11 Algorithm and its Relevance
The X11 algorithm, while not as commonly discussed as Ethereum’s Proof-of-Work or Bitcoin’s SHA-256, holds a unique place in the crypto landscape. Designed as a more energy-efficient and secure alternative, X11 has found its niche, especially in the DeFi space. Let’s explore the X11 algorithm and its significance in DeFi.
What is the X11 Algorithm?
X11 is a chained hashing algorithm used for the proof-of-work consensus mechanism in various cryptocurrencies. It employs a sequence of eleven scientific hashing algorithms, which makes it one of the safest and more sophisticated cryptographic hashes in use by modern cryptocurrencies.
Key Features of X11:
- Enhanced Security: The chained hashing approach provides a higher degree of security. Even if one of the eleven hashing functions is compromised, the entire chain remains secure.
- Energy Efficiency: X11 is known for its energy efficiency compared to other algorithms. This makes it more environmentally friendly and cost-effective for miners.
- ASIC Resistance: Initially, X11 was designed to be resistant to ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) miners, promoting decentralization. However, over time, ASICs for X11 have been developed, but the algorithm still offers a more level playing field compared to others.
X11 in DeFi Projects
Several DeFi projects have recognized the benefits of the X11 algorithm and integrated it into their platforms. Here’s how:
- Security: Given the high stakes in DeFi, where smart contracts handle millions (or billions) of dollars, the enhanced security of X11 is a significant advantage.
- Sustainability: As the crypto community becomes more conscious of environmental impacts, the energy efficiency of X11 makes it a preferred choice for green projects.
- Diverse Mining Community: The relative ASIC resistance of X11 (especially in its early days) has led to a more decentralized and diverse mining community, aligning with the ethos of DeFi.
Challenges and Considerations
While X11 offers several advantages, it’s not without challenges:
- ASIC Dominance: Over time, the development of X11 ASIC miners has led to concerns about centralization and the sidelining of GPU miners.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating X11 into DeFi projects requires expertise, given its unique chained hashing approach.
- Market Perception: Despite its benefits, X11 is less known than algorithms like Proof-of-Work or Proof-of-Stake. Educating the community and stakeholders is crucial for projects using X11.
Designing Sustainable X11-based DeFi Projects
The integration of the X11 algorithm into DeFi projects presents both opportunities and challenges. For projects to thrive, it’s essential to design them with sustainability in mind. This section will explore the key considerations and best practices for creating enduring X11-based DeFi platforms.
Understanding Sustainability in DeFi
Sustainability in the context of DeFi doesn’t just refer to environmental considerations. It encompasses a project’s long-term viability, security, community engagement, and adaptability to market changes.
Key Considerations for Sustainability:
- Robust Security Protocols: Given the X11 algorithm’s inherent security features, projects should further bolster security by regularly auditing smart contracts, implementing multi-signature wallets, and encouraging bug bounty programs.
- Community Engagement: A thriving community is the backbone of any successful DeFi project. Regular updates, transparent communication, and community-driven governance can foster trust and loyalty among users.
- Economic Incentives: Designing tokenomics that reward long-term participation can deter pump-and-dump schemes. This includes staking rewards, liquidity mining, and governance voting rights.
- Interoperability: As the crypto ecosystem grows, projects that can seamlessly integrate with other platforms and chains will have a competitive edge. Consider building bridges or partnerships with other prominent DeFi projects.
- Continuous Innovation: The DeFi space is rapidly evolving. Projects should be ready to adapt, whether it’s integrating Layer 2 solutions for scalability or offering new financial products.
Challenges and the Way Forward
While the potential of X11-based DeFi projects is vast, they face challenges like market adoption, regulatory scrutiny, and technological hurdles. However, with a clear vision, community involvement, and a commitment to innovation, these challenges can be transformed into growth opportunities.
Risks and Challenges in DeFi
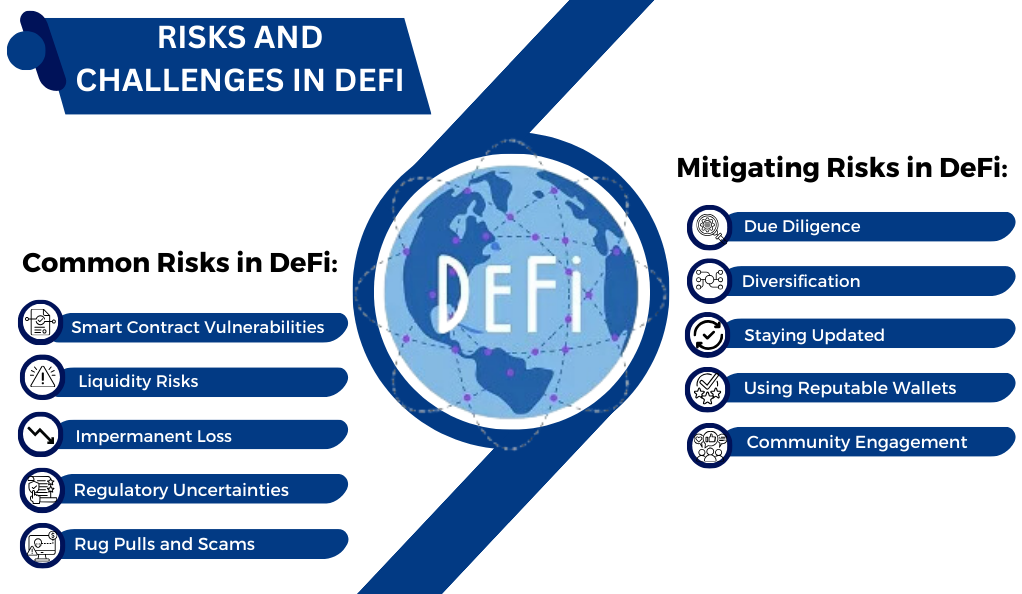
While the DeFi sector has shown immense promise and has revolutionized the way we perceive financial systems, it’s not without its set of challenges and risks. For investors, developers, and users, understanding these risks is paramount to navigate the DeFi landscape safely and effectively.
Common Risks in DeFi:
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: As DeFi platforms rely heavily on smart contracts, any vulnerability or bug in the code can lead to significant losses. Notable incidents, such as the DAO hack, underscore the importance of rigorous smart contract auditing.
- Liquidity Risks: Some DeFi platforms may face liquidity crunches, especially if a large number of users decide to withdraw their funds simultaneously. This can lead to a cascading effect, causing panic and destabilizing the platform.
- Impermanent Loss: In liquidity pools, especially in Automated Market Makers (AMMs) like Uniswap, liquidity providers can face impermanent loss. This occurs when the price of tokens inside a pool diverges in any direction away from when they were deposited.
- Regulatory Uncertainties: The decentralized nature of DeFi often puts it in a gray regulatory zone. Changes in regulatory stances, especially in major economies, can impact the adoption and growth of DeFi platforms.
- Rug Pulls and Scams: The open-source and permissionless nature of DeFi also means that malicious actors can launch projects with the intent to defraud users. Such projects often disappear after accumulating funds, leaving users with significant losses.
Mitigating Risks in DeFi:
- Due Diligence: Before interacting with any DeFi platform, users should conduct thorough research. This includes checking for smart contract audits, understanding tokenomics, and reading community feedback.
- Diversification: Just as with traditional investments, diversifying holdings across various DeFi platforms can mitigate potential losses.
- Staying Updated: The DeFi landscape is dynamic. Regularly updating oneself with the latest news, regulatory changes, and technological advancements can help in making informed decisions.
- Using Reputable Wallets: Engaging with DeFi through secure and reputable wallets can add an additional layer of security.
- Community Engagement: Being active in a project’s community can provide real-time insights, updates, and a sense of the project’s legitimacy.
Conclusion
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) stands at the crossroads of innovation, promising a financial landscape that is more inclusive, transparent, and empowering. The intricate dance of tokenomics, combined with advanced algorithms like X11, has been instrumental in shaping this new era of finance. As we navigate this evolving domain, the lessons learned, challenges faced, and successes celebrated will collectively pave the way for a future where financial tools and services are accessible to all, devoid of traditional barriers. The journey of DeFi is not just about technology or economics; it’s a testament to the human spirit’s relentless pursuit of decentralization, autonomy, and equitable financial systems for all.
At axerunners.com, our goal is to furnish well-rounded and trustworthy information regarding cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and stocks. Nonetheless, we avoid providing financial advice and instead encourage users to conduct their own research and meticulous verification.
Read More












