In the rapidly evolving world of cryptocurrencies, the importance of understanding the intricacies of crypto wallets cannot be overstated. These wallets, digital tools designed to store and manage one’s cryptocurrency holdings, are the gatekeepers of the crypto realm. They not only ensure the safety of one’s digital assets but also play a pivotal role in how these assets are accessed, transferred, and utilized.
However, as with any financial tool, crypto wallets don’t exist in a vacuum. They are intricately tied to the legal and regulatory frameworks of various jurisdictions. This intertwining of technology and law brings forth a myriad of questions: Who truly owns the digital assets? What happens if a wallet provider goes bankrupt? What are the legal ramifications of losing access to a wallet?
To answer these questions and more, it’s essential first to understand the two primary types of crypto wallets: custodial and non-custodial. While both serve the primary function of storing cryptocurrencies, they differ significantly in their operation, security measures, and the degree of control they offer to the user.
| Feature | Custodial Wallets | Non-Custodial Wallets |
|---|---|---|
| Control Over Private Keys | Held by a third-party provider | Held by the user |
| Security | Dependent on the provider’s measures | Dependent on user’s measures |
| Ease of Use | Generally user-friendly with a simple interface | Might require a deeper understanding of crypto |
| Recovery Options | Often available through the provider | Limited; dependent on seed phrases |
| Legal Implications | Subject to regulations of the provider’s jurisdiction | Often falls under the user’s jurisdiction |
Understanding Crypto Wallet Basics
Before diving deeper into the distinctions between custodial and non-custodial wallets, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental workings of a crypto wallet. At its core, a crypto wallet is a digital tool, but it’s quite different from the traditional wallets we carry in our pockets.
How Crypto Wallets Work: Beyond the Basics
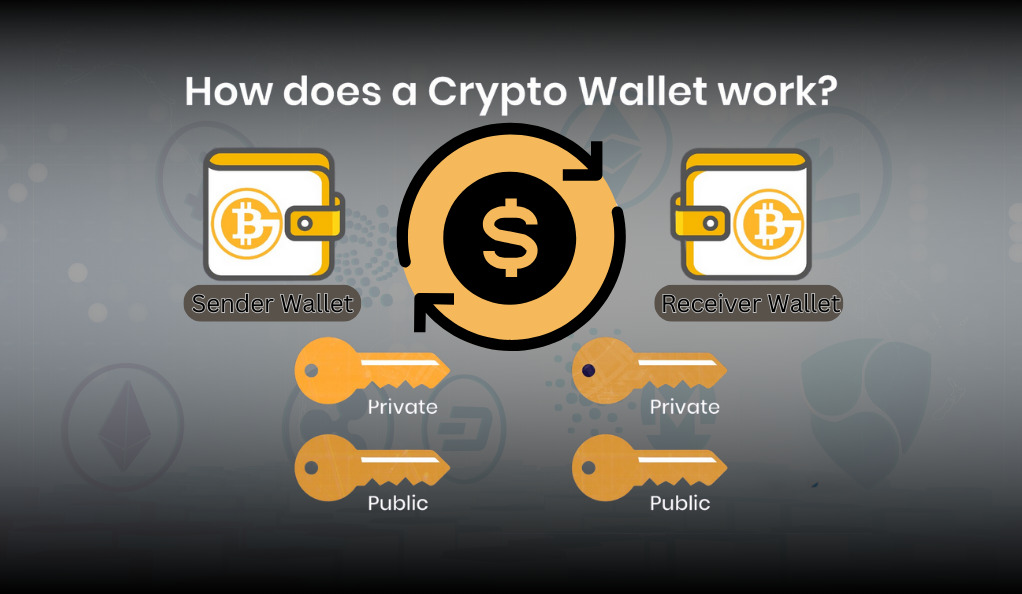
Every cryptocurrency transaction involves two key components: a public key and a private key. Think of the public key as an address that others can see and send funds to, much like an email address. The private key, on the other hand, is akin to a password that gives the holder access to the funds and the ability to send them. It’s imperative to keep this private key secure, as anyone with access to it can control the associated funds.
The Misconception: Wallets Don’t Hold Funds
A common misconception is that crypto wallets store digital coins, much like a physical wallet holds cash. In reality, cryptocurrencies always remain on the blockchain. What the wallet holds are the cryptographic keys (public and private) that allow a user to access and manage their funds on the blockchain.
The Role of Wallet Addresses
In addition to public and private keys, crypto wallets generate a wallet address. This address, derived from the public key, is what users share to receive funds. It’s a more user-friendly version of the public key, often represented as a string of alphanumeric characters or a QR code.
Custodial Wallets: A Deep Dive
When we talk about custodial wallets, we refer to a system where the private keys (and, by extension, the control of the funds) are held by a third-party entity, such as a cryptocurrency exchange or a specialized wallet service. This setup offers a user-friendly experience, especially for those new to the crypto world, as it abstracts away some of the complexities of managing private keys.
Benefits of Custodial Wallets
- Ease of Use: For many, the user interface of custodial wallets resembles that of online banking or digital payment apps, making the transition to crypto smoother.
- Backup and Recovery: If you forget your password or lose access to your account, the custodial provider often has mechanisms to help you recover your funds.
- Integrated Services: Many custodial wallets, especially those provided by exchanges, offer integrated services like trading, staking, and earning interest.
The Trust Factor
The primary trade-off with custodial wallets is trust. Users must trust the third-party provider to:
- Safeguard the private keys.
- Not to engage in malicious activities.
- Implement robust security measures against external threats.
While many reputable providers go to great lengths to ensure security, the history of crypto has instances of exchanges and wallet providers being hacked or mismanaging funds.
Non-Custodial Wallets: Full Control in Your Hands

Venturing into the realm of non-custodial wallets, we encounter a system that stands in stark contrast to its custodial counterpart. Here, the user retains full control over their private keys and, by extension, their funds. This control comes with both its advantages and responsibilities.
The Essence of Non-Custodial Wallets
A non-custodial wallet, often termed a “self-custody” wallet, empowers the user with complete autonomy over their cryptocurrency holdings. Unlike custodial wallets, where a third party oversees the private keys, non-custodial wallets ensure that only the user has access to these keys.
Forms of Non-Custodial Wallets
Non-custodial wallets can manifest in various forms:
- Software Wallets: These are applications or software installed on a computer or mobile device. They generate and store the private keys on the device itself.
- Hardware Wallets: Physical devices, often resembling USB drives, that securely generate and store private keys offline. They are considered one of the most secure wallet types since they’re immune to online hacking attempts.
- Paper Wallets: A physical document containing both the public and private keys. It’s a form of cold storage, as the keys aren’t stored on a computer or any internet-connected device.
The Double-Edged Sword of Control
While having control over one’s private keys offers unparalleled security, it also comes with its set of challenges:
- Loss of Seed Phrase: Most non-custodial wallets provide a seed phrase, a series of words that can regenerate the wallet’s private key. If a user loses this phrase and their wallet access, they lose their funds permanently.
- User Security: The onus of security lies entirely with the user. They must ensure their private keys or seed phrases are stored securely and are not susceptible to theft or loss.
The Power of Decentralization
One of the core tenets of cryptocurrency is decentralization, and non-custodial wallets embody this principle. Without intermediaries or centralized entities holding the keys, users experience the true essence of what cryptocurrencies aim to achieve: a decentralized, peer-to-peer financial system where individuals have full sovereignty over their assets.
Legal Implications and Regulations
As the world of cryptocurrency continues to intersect with traditional finance, the legal landscape surrounding crypto wallets becomes increasingly intricate. Both custodial and non-custodial wallets find themselves under the scrutiny of regulators worldwide.
The Regulatory View on Custodial Wallets
Given their centralized nature, custodial wallets often fall under the purview of financial regulations similar to banks or financial institutions. They may be required to:
- Perform KYC (Know Your Customer) Procedures: Verifying the identity of their users to prevent illegal activities.
- Adhere to AML (Anti-Money Laundering) Policies: Monitoring and reporting suspicious transactions to combat money laundering.
- Ensure Consumer Protection: Safeguarding users’ funds and providing transparency in their operations.
Non-Custodial Wallets: A Gray Area
The decentralized nature of non-custodial wallets presents a challenge for regulators. Since there’s no central entity to oversee or regulate, these wallets often operate in a legal gray area. However, users might still face tax implications or reporting requirements based on their jurisdiction.
Security Measures and Best Practices
In the vast and often unpredictable world of cryptocurrencies, security remains paramount. Whether you’re a seasoned crypto enthusiast or a newcomer, understanding and implementing robust security measures can be the difference between safeguarding your assets and suffering potential losses.
The Layers of Security
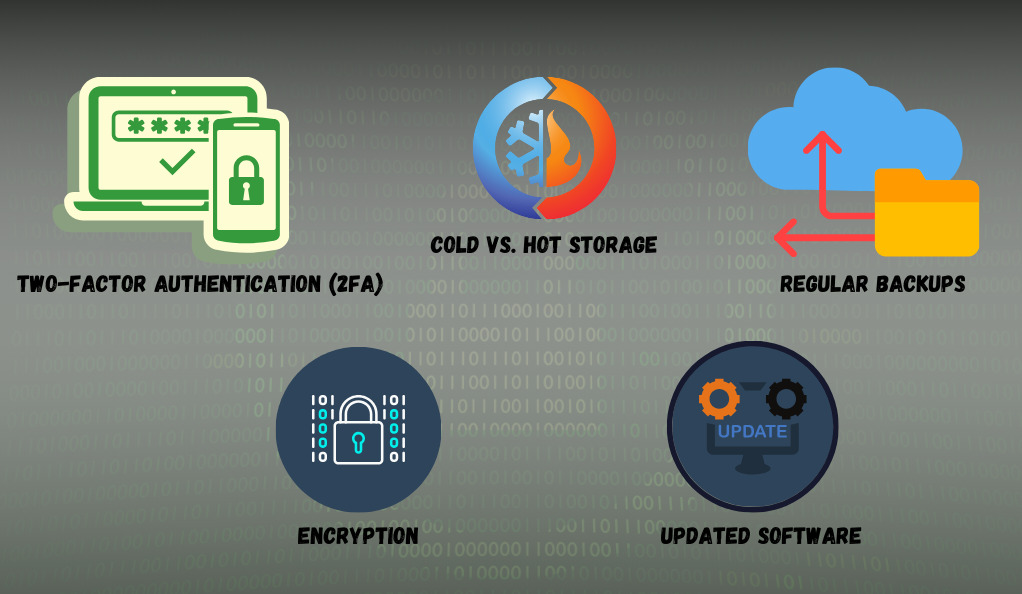
While the fundamental principles of security remain consistent across both custodial and non-custodial wallets, their application can vary. Here’s a breakdown:
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): An additional layer of security where users must provide two types of identification before accessing their funds. This often combines something they know (a password) with something they have (a mobile device or a hardware token).
- Cold vs. Hot Storage:
- Cold Storage: Refers to keeping private keys completely offline, making them immune to online hacks. Hardware and paper wallets are typical forms of cold storage.
- Hot Storage: Refers to wallets connected to the internet, like software wallets or exchange wallets. While they offer more convenience, they are also more vulnerable to online threats.
- Regular Backups: Regularly backing up a wallet ensures that even in the event of device failure, the wallet and its contents can be restored.
- Encryption: Encrypting a wallet means it can’t be accessed without a password, adding an extra layer of defense against unauthorized access.
- Updated Software: Keeping the wallet software updated ensures that it has the latest security enhancements and bug fixes.
Best Practices for Optimal Security
- Never Share Private Keys or Seed Phrases: This is the golden rule. Sharing these can lead to loss of funds.
- Use Trusted Networks: Avoid accessing wallets from public Wi-Fi or shared computers.
- Beware of Phishing: Always double-check URLs and be wary of unsolicited communications asking for private keys, seed phrases, or other sensitive information.
- Diversify Storage: Instead of storing all assets in one wallet, consider diversifying across multiple wallets or storage solutions.
Due Diligence and Personal Research
In the dynamic world of cryptocurrencies, where the only constant is change, due diligence becomes the bedrock of any informed decision. While this article provides a comprehensive overview of crypto wallets and their associated regulations, it’s essential to remember that the crypto landscape is continually evolving. New technologies emerge, regulations shift, and market dynamics can change rapidly.
The Importance of Continuous Learning
- Stay Updated: Cryptocurrency and blockchain technology are still in their infancy. New developments, both in terms of technology and regulations, occur frequently. Subscribing to reputable crypto news outlets, forums, and communities can help you stay abreast of the latest trends.
- Question Everything: In the decentralized world of crypto, not everything is as it seems. Before making decisions, especially those involving significant sums, always seek multiple sources of information and verify claims.
- Engage with the Community: The crypto community is vast, diverse, and often very knowledgeable. Engaging in discussions, asking questions, and sharing experiences can provide invaluable insights.
Navigating the Sea of Information
With the explosion of interest in cryptocurrencies, there’s no shortage of information available. However, not all sources are created equal. Here are some tips to navigate this sea of information:
- Reputable Sources: Stick to well-known, reputable crypto publications and avoid sources that have a history of spreading misinformation or have undisclosed biases.
- Expert Opinions: While experts can provide valuable insights, it’s essential to remember that no one can predict market movements with absolute certainty. Use expert opinions as one of many tools in your decision-making arsenal.
- Avoid Hype: The crypto world is notorious for its hype cycles. It’s easy to get caught up in the excitement, but always ground your decisions in research and logic rather than emotion.
Conclusion
The realm of cryptocurrencies and their associated wallets is both thrilling and complex. As we stand at the forefront of this financial revolution, the choices we make are empowered by knowledge but also come with inherent responsibilities.
Crypto wallets, whether custodial or non-custodial, are the gatekeepers of our digital assets. Their selection and management require a blend of due diligence and continuous learning. As the crypto landscape evolves, staying informed and making well-researched decisions become paramount.
In essence, the world of crypto offers unparalleled opportunities, but it also demands caution and vigilance. As we look ahead, it’s clear that crypto wallets will play a central role in shaping our financial future. Embrace the journey, stay informed, and always prioritize security.
At axerunners.com, our goal is to furnish well-rounded and trustworthy information regarding cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and stocks. Nonetheless, we avoid providing financial advice and instead encourage users to conduct their own research and meticulous verification.
Read More