Cryptocurrency mining, often simply referred to as “crypto mining,” is a complex process where transactions for various cryptocurrencies are verified and added to the blockchain, a public ledger. This process involves solving complex mathematical problems using computational power. Let’s delve deeper into this intriguing world.
What is Crypto Mining?

Crypto mining is the digital equivalent of mining for gold, but instead of physical digging, miners use computers to solve complex mathematical problems. When these problems are solved, new blocks of transactions are added to the blockchain, and miners are rewarded with a certain amount of cryptocurrency for their efforts.
How Does It Work?
a. Transaction Verification
Before any crypto transaction is added to the blockchain, it needs to be verified. This is done by miners. They take transactions, verify them as legitimate, and spread them across the network.
b. Proof of Work
To add a block to the blockchain, miners must solve a complex mathematical problem, which requires finding a number that, when hashed, produces a specific result. This process is known as proof of work because it proves that a miner has done the work to receive a reward.
c. Mining Reward
Once the problem is solved, the miner shares the solution with other nodes in the network. If the solution is correct, a new block is added to the blockchain, and the miner is rewarded with a certain amount of cryptocurrency.
Mining Methods
a. Solo Mining
In solo mining, an individual miner uses their resources to mine blocks. While the reward is significant since the miner doesn’t have to share it, the chances of solving a block are lower due to the high competition.
b. Pool Mining
Miners join forces to form a pool. They combine their computational power to increase their chances of solving blocks. When the pool solves a block, the reward is divided among the members based on their contribution.
Comparison Table: Solo Mining vs. Pool Mining
| Criteria | Solo Mining | Pool Mining |
|---|---|---|
| Reward Size | High (full block reward) | Divided based on contribution |
| Consistency | Less frequent rewards | More consistent, smaller rewards |
| Resources | Requires significant computational power | Combined resources increase success rate |
| Difficulty | High competition | Easier due to combined effort |
Equipment Needed for Mining
1. GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)
The NVIDIA RTX 4090 and AMD RX 6900 XT are considered among the best GPUs for various reasons, particularly in contexts like gaming, professional graphic workloads, and cryptocurrency mining:
a. NVIDIA RTX 4090

- Performance: This GPU is built on NVIDIA’s latest ‘Ampere’ architecture, which offers significant improvements over its predecessors in terms of processing power and efficiency.
- Ray Tracing and DLSS: It supports advanced features like real-time ray tracing and Deep Learning Super Sampling (DLSS). Ray tracing enhances realistic lighting and reflections, while DLSS uses AI to upscale images, improving performance without compromising on image quality.
- Mining Efficiency: For cryptocurrency mining, the RTX 4090 delivers high hash rates, which means it can compute more calculations per second, leading to potentially more mined cryptocurrency. It also has a reputation for being energy-efficient, meaning it can deliver high performance while keeping electricity costs relatively lower.
- Tensor Cores: These are specialized cores that accelerate deep learning algorithms, beneficial not just for DLSS in gaming, but also for professional AI and data science workloads.
b. AMD RX 6900 XT

- Performance: AMD’s RX 6900 XT is based on the RDNA 2 architecture, which provides a substantial boost in performance and power efficiency compared to its previous generation GPUs.
- Price-to-Performance Ratio: While it competes with the RTX 4090 in terms of raw performance, it often comes at a lower price point, offering a competitive price-to-performance ratio that appeals to many consumers.
- Smart Access Memory (SAM): This feature allows the CPU to access the full GPU memory, potentially boosting performance in certain tasks.
- Mining Capability: Although it might be slightly less efficient in power consumption compared to the RTX 4090, it still offers high hash rates, making it a viable option for cryptocurrency mining.
- Software Ecosystem: AMD’s software, like the Radeon Software suite, has been praised for its user-friendly interface and features like Radeon Boost and Radeon Anti-Lag, which can improve gaming experiences.
Both GPUs represent the high end of the market and are suitable for users who require premium performance for tasks such as 3D rendering, complex simulations, high-resolution and high-framerate gaming, and cryptocurrency mining. The choice between them may come down to specific needs, brand preference, budget, and the importance of certain features like NVIDIA’s ray tracing versus AMD’s SAM.
2. CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The CPU’s role in a mining rig is generally to support the GPUs, which do the bulk of the mining work. However, the CPU is still an important part of the system, especially when it comes to overall system responsiveness, running the mining software, and handling any other tasks the rig might be performing simultaneously. Here’s why the AMD Ryzen 9 5950X and Intel Core i5-12600K are suitable for such setups:
a. AMD Ryzen 9 5950X

- Core Count: With 16 cores and 32 threads, this CPU is well-suited for multitasking and handling complex operations beyond mining, such as data analysis, video editing, or running virtual machines.
- High-End Performance: It is part of AMD’s high-end desktop CPU line-up, offering excellent performance not just for mining rig management but also for other CPU-intensive tasks.
- Versatility: Users who want their mining rigs to double up for other tasks may find the Ryzen 9 5950X a good investment because of its robust performance capabilities.
b. Intel Core i5-12600K

- Cost-Efficiency: The i5-12600K is a mid-range CPU that provides good performance for its price, making it an excellent option for those on a tighter budget.
- Hybrid Architecture: This CPU features Intel’s new hybrid architecture with Performance-cores (P-cores) and Efficient-cores (E-cores), which can efficiently manage different types of workloads.
- Power Consumption: It generally has lower power consumption than higher-end CPUs, which might be beneficial for mining rigs where power efficiency is a key concern.
- Mining Rig Suitability: While not as powerful as the Ryzen 9 5950X, it still offers more than enough capability for running a mining rig, where the CPU is not the primary workhorse.
The choice between these CPUs would depend on the user’s specific needs and budget. If the rig is solely for mining and cost and power efficiency are the primary concerns, the Intel Core i5-12600K might be the better choice. However, if the rig will be used for other high-performance tasks, or if there’s a need for a more future-proof system, the AMD Ryzen 9 5950X could be worth the extra investment.
3. Motherboard
Motherboards are crucial for mining rigs as they determine how many GPUs can be connected and ensure stability and connectivity for all components. Here’s why the ASUS B250 Mining Expert and ASRock H110 Pro BTC+ stand out:
a. ASUS B250 Mining Expert
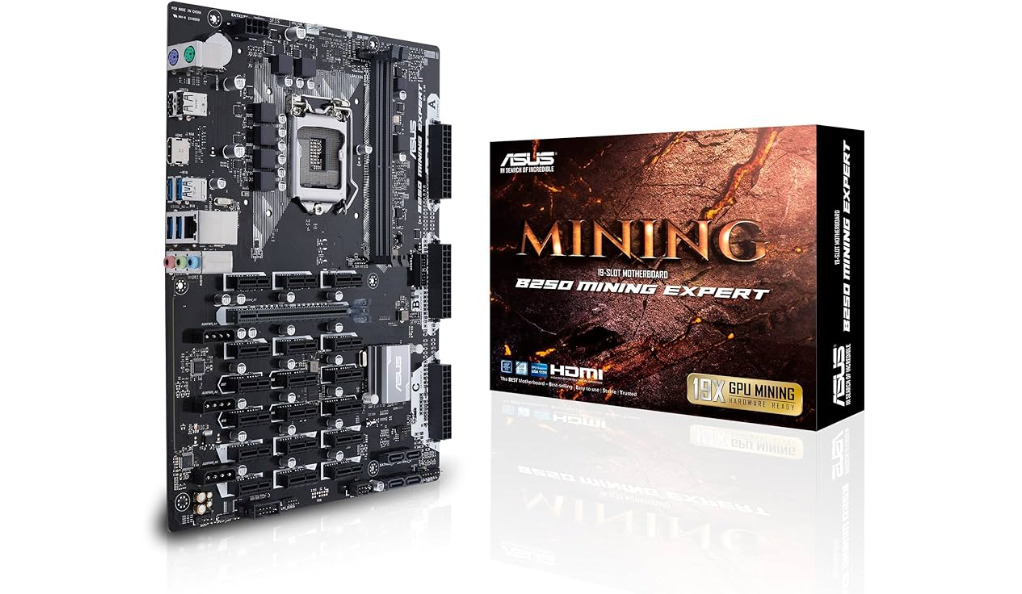

- GPU Support: It supports up to 19 GPUs, which is unparalleled for mining motherboards. This allows for significant scalability in mining operations.
- Mining Optimized: The board is designed with mining-specific features, such as a unique BIOS setup that simplifies the process of setting up a mining rig.
- Stable Power Delivery: It includes three 24-pin power connectors to ensure a stable power supply to all connected GPUs, which is critical when running so many cards.
- Efficient Slot Layout: The PCIe slots are spaced to provide ample room for airflow, which is vital for maintaining the GPUs’ temperatures when many are used simultaneously.
b. ASRock H110 Pro BTC+
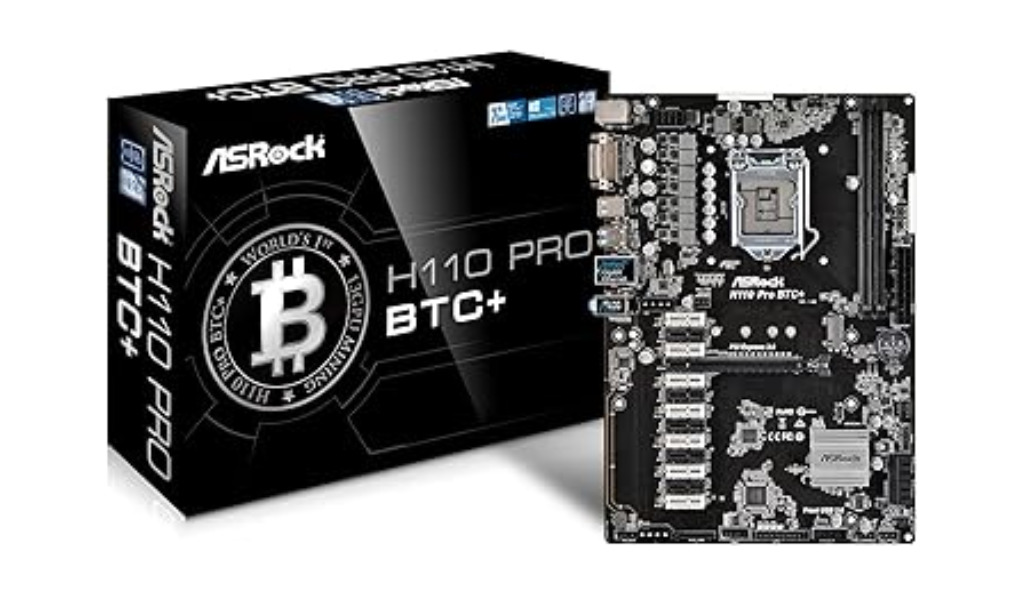

- High GPU Capacity: While not as high as the ASUS B250, supporting up to 13 GPUs is still significant for building a large-scale mining operation.
- Cost-Effectiveness: It’s often more affordable than higher-end mining motherboards, offering a good balance between features and price.
- Durability: ASRock is known for durability, which is crucial when the motherboard is running at full capacity with multiple GPUs.
- Compatibility: It’s compatible with a wide range of CPUs, which gives miners flexibility in choosing the rest of the rig’s components.
Both motherboards are tailored to miners looking to maximize their rig’s GPU capacity. The ASUS B250 Mining Expert is the go-to for those looking to push the limits of GPU expansion, while the ASRock H110 Pro BTC+ is a strong choice for those who want a slightly smaller yet efficient setup. The decision between the two would typically be influenced by the scale of the mining operation, budget, and the desired number of GPUs in the rig.
4. RAM (Random Access Memory)
For a mining rig, RAM is generally not a performance bottleneck, as the mining performance is predominantly dependent on the GPU. However, having sufficient RAM is still important to ensure smooth operation of the system. Here’s why Corsair Vengeance LPX 16GB is a suitable choice:
- Sufficient Capacity: 16GB of RAM is more than adequate for mining and will comfortably handle the operating system and mining software without any bottlenecks.
- Stability and Reliability: Corsair is a well-known brand for producing high-quality memory modules that offer stability and reliability, which is crucial for a system that runs 24/7.
- High-Speed Memory: The Vengeance LPX series is designed for high-performance overclocking with a heat spreader for cooling. While overclocking is more CPU and GPU-centric, stable and fast RAM can help maintain overall system performance.
- Compatibility: This RAM has a low-profile design that ensures wide compatibility with bigger CPU coolers, which is important if the mining rig also doubles for CPU-intensive tasks.
- Future Proofing: Even though more RAM doesn’t improve mining performance, having 16GB is considered somewhat future-proof, should the rig be repurposed for other tasks in the future that may require more memory.
In a mining setup, once the minimum required RAM is installed, the law of diminishing returns kicks in quickly; additional RAM won’t improve mining output but will consume more power and add to costs. Therefore, a balanced approach like opting for the Corsair Vengeance LPX 16GB strikes a good middle ground between performance and cost.
5. Storage
In a mining rig, storage is primarily used for the operating system, mining software, and potentially the blockchain data, depending on the cryptocurrency being mined. Here’s why the Samsung 970 EVO Plus SSD 250GB is an appropriate choice for such a setup:

- Speed: The Samsung 970 EVO Plus is an NVMe SSD with read/write speeds significantly faster than traditional SATA SSDs or HDDs, which means the system will boot up quickly and run smoothly.
- Durability: SSDs, in general, are more durable than HDDs because they have no moving parts, and the Samsung 970 EVO Plus is known for its reliability, which is important for a mining rig that operates continuously.
- Sufficient Storage: For mining, you don’t need a lot of storage, so 250GB is ample space for the operating system, mining software, and any other small tools or data you might need.
- Efficiency: SSDs consume less power than HDDs, which can be beneficial for a mining operation where efficiency is key to maximizing profitability.
- Form Factor: Being an M.2 drive, it takes up less physical space and can help with building a more compact rig, which could be important if space is at a premium.
The Samsung 970 EVO Plus 250GB strikes a balance between performance and capacity, providing fast data access speeds without adding unnecessary storage that would remain unused in a mining rig. This makes it an ideal choice for a dedicated mining system.
6. Power Supply Unit (PSU)
For mining rigs that operate multiple high-end GPUs, a robust and efficient power supply unit (PSU) is critical. Here’s why the Corsair HX1200 and the EVGA SuperNOVA 1300 G2 are recommended:
a. Corsair HX1200
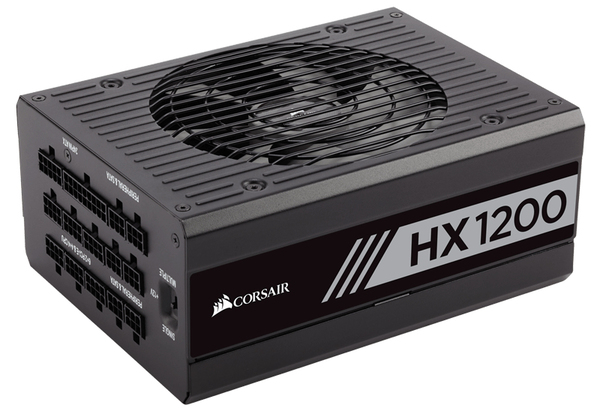

- High Wattage: With 1200W, the HX1200 can support multiple GPUs, which is essential for a mining rig running several RTX 4090s or other high-end GPUs.
- Efficiency: It has an 80 PLUS Platinum efficiency rating, meaning it runs at around 92% efficiency at 50% load. Efficient PSUs waste less electricity and produce less heat, which is vital for the continuous operation of a mining rig.
- Modular Design: The fully modular cable design allows you to use only the cables you need, which helps with building a clean rig and improving airflow.
- Build Quality and Reliability: Corsair is known for good build quality and reliable components, which translates to fewer maintenance issues and a longer lifespan.
b. EVGA SuperNOVA 1300 G2:

- Higher Wattage: With 1300W, it offers slightly more headroom than the Corsair HX1200, which could be beneficial if you’re running a rig that’s close to the power limit.
- Efficiency: This PSU also has an 80 PLUS Gold rating, ensuring high energy efficiency (up to 90% under typical loads).
- Stability: It is well-regarded for its stable power delivery, which is crucial when running multiple GPUs to prevent fluctuations that could cause damage or reduce the lifespan of components.
- Customer Support and Warranty: EVGA has a strong reputation for customer service and offers a long warranty period, which is reassuring for a component that’s a critical part of a mining rig’s infrastructure.
Choosing between these two PSUs would typically come down to specific power requirements, budget, and personal brand preference. Both are capable of handling high loads and come from reputable brands with good support and warranty policies, making them solid choices for serious mining operations.
7. Cooling System
Cooling is paramount in a mining rig to ensure longevity and optimal performance of GPUs which operate under heavy load for extended periods. Here’s why the Noctua NF-A12x25 PWM and Corsair Hydro Series H150i are suitable choices for cooling solutions:
a. Noctua NF-A12x25 PWM:

- Airflow and Static Pressure: These fans are engineered to deliver a high airflow and static pressure, meaning they are effective at cooling components even when there’s resistance, like through a heatsink or radiator.
- Quiet Operation: Noctua fans are renowned for their quiet operation, which is a significant advantage in maintaining a low noise level, especially important in a setup with multiple fans.
- Build Quality: Known for exceptional build quality and long-term durability, which is crucial for mining rigs that operate 24/7.
- PWM Control: The Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) feature allows for precise speed control, enabling the fans to run at lower speeds when full power isn’t needed, reducing noise and power consumption.
b. Corsair Hydro Series H150i:

- Liquid Cooling: This all-in-one (AIO) liquid cooler can manage the high thermal loads of densely packed, high-performance GPUs, which is often necessary in a compact high-density mining rig.
- Large Radiator: The H150i comes with a large radiator that provides a substantial cooling surface area, which is beneficial for dissipating heat from multiple GPUs.
- Integrated Pump and Fans: It includes a pump and PWM-controlled fans, providing a complete cooling solution that’s relatively easy to install.
- Corsair iCUE Compatibility: The cooler is compatible with Corsair’s iCUE software, allowing for precise control over the cooling performance and fan speeds, and even enabling monitoring of temperatures.
In choosing between air and liquid cooling, it’s essential to consider the specific needs of the mining rig. For rigs that are not extremely densely packed and have room for good airflow, high-quality air cooling like the Noctua NF-A12x25 PWM fans may suffice. However, for high-density rigs or in scenarios where the ambient temperature is high, an AIO liquid cooling system like the Corsair Hydro Series H150i may be more appropriate due to its superior cooling capacity.
8. Mining Frame
A mining frame is the skeleton of a mining rig; it holds all the components together and ensures they are adequately cooled and easily accessible. The Veddha V3C 8-GPU Mining Case is a popular choice for several reasons:

- Capacity: It can house up to 8 GPUs, which is suitable for a mid-to-large scale mining operation.
- Airflow Design: The open-air design of the Veddha V3C allows for unobstructed airflow, which is critical for cooling high-performance GPUs.
- Sturdy Construction: Made of aluminum, it’s both lightweight and sturdy, providing a solid foundation for the valuable components it will hold.
- Ease of Assembly and Accessibility: The frame is designed to be easy to assemble and provides easy access to components, simplifying maintenance and upgrades.
- Stackability: If you’re expanding your mining operation, these frames can be stacked, saving space and allowing for a cleaner setup.
- Cooling Support: It includes locations for mounting fans, further supporting the cooling of the GPUs, which is essential for the longevity and efficiency of a mining rig.
A well-designed mining frame like the Veddha V3C contributes to the overall efficiency and safety of the mining operation by ensuring components are kept cool and secure.
9. Operating System and Mining Software
The operating system (OS) and mining software are central to the management and efficiency of a mining rig. Here’s how HiveOS and Windows 10 stack up in this context:
a. HiveOS:

- Mining-Focused: HiveOS is designed specifically for mining, which means it’s optimized for stability and performance in long-term mining operations.
- User-Friendly: It features a user-friendly interface that simplifies the management of large mining farms as well as single rigs.
- Comprehensive Dashboard: Provides a comprehensive dashboard for monitoring and controlling all aspects of the mining operation, including GPU temperatures, fan speeds, hash rates, and more.
- Overclocking Tools: Includes built-in tools for overclocking GPUs and adjusting power settings directly within the OS, which can be crucial for optimizing mining performance and efficiency.
- Wide Mining Software Support: HiveOS supports a variety of mining software, allowing miners to switch between different cryptocurrencies and algorithms with ease.
- Remote Management: Offers robust remote management features, enabling miners to manage their rigs from anywhere.
b. Windows 10:

- Familiarity: Many users prefer Windows 10 because of their familiarity with the Windows environment, making it easier to set up and troubleshoot.
- Software Compatibility: Windows 10 supports a wide range of mining software as well, and it can be easier to find drivers for a variety of hardware components.
- Versatility: Beyond mining, Windows 10 can run all types of software, so the mining rig can double as a workstation for other tasks if needed.
- Graphical User Interface (GUI): The GUI is user-friendly and well-suited for those who are not as comfortable with command-line interfaces.
- Updates and Support: Regular updates from Microsoft ensure security and stability, although sometimes updates can interfere with mining operations if not managed properly.
Choosing between HiveOS and Windows 10 often boils down to personal preference and the specific needs of the mining operation. HiveOS is tailored for mining and might offer better out-of-the-box optimization, while Windows 10 provides a more general-purpose environment with the potential for a broader range of tasks.
10. Mining Pool Membership
Joining a mining pool can significantly increase the chances of earning mining rewards, especially for individual miners who might find it difficult to compete with large-scale mining operations. Here’s why Ethermine and NiceHash are notable options:
a. Ethermine:

- High Reputation: Ethermine is one of the largest mining pools for Ethereum, known for its reliability and trustworthiness.
- Low Fees: It offers competitive fees for participating in the pool, which is an important consideration for miners looking to maximize their profits.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Provides real-time statistics on hash rates, earnings, and other relevant metrics, allowing miners to closely monitor their rigs’ performance.
- Payout Options: Ethermine has various payout options, including the traditional Pay Per Last N Shares (PPLNS) system, which benefits consistent miners.
- Global Network: The pool has servers located around the world, ensuring low latency and thus more efficient mining for participants globally.
b. NiceHash:

- Flexibility: NiceHash is unique in that it allows miners to mine various cryptocurrencies but get paid in Bitcoin, offering flexibility in earnings.
- Ease of Use: It is user-friendly, especially for beginners, with a straightforward setup process and intuitive user interface.
- Mining and Trading: NiceHash combines mining and cryptocurrency exchange features, allowing users to sell or buy hashing power on their marketplace.
- Profitability Switching: The service automatically switches to mining the most profitable cryptocurrency at any given time based on the market, which can optimize earnings without manual intervention.
- Regular Payouts: NiceHash provides regular payouts, an important feature for miners who wish to have consistent earnings.
Both Ethermine and NiceHash cater to different needs and preferences. Ethermine is a traditional mining pool that is well-suited for those focused on Ethereum, while NiceHash is more about flexibility and ease, especially for those who prefer their mining rewards in Bitcoin. The choice of mining pool will depend on the individual miner’s goals, the cryptocurrencies they are interested in, and the payment types they prefer.
Challenges in Crypto Mining
a. High Energy Consumption
Mining requires significant computational power, leading to high electricity costs.
b. Hardware Costs
Efficient mining requires investment in high-end hardware, which can be expensive.
c. Market Volatility
The value of rewards can fluctuate based on the cryptocurrency’s market value.
Understanding ASIC Miners
Application-Specific Integrated Circuits, commonly known as ASICs, have become the cornerstone of the cryptocurrency mining industry due to their unparalleled efficiency and processing power. Let’s dive deep into the world of ASIC miners and understand their significance, workings, and impact on the crypto mining landscape.
What are ASIC Miners?
ASIC miners are specialized hardware devices designed for a specific application—in this case, cryptocurrency mining. Unlike general-purpose devices like CPUs (Central Processing Units) and GPUs (Graphics Processing Units), ASICs are optimized to perform a single task, making them highly efficient for that particular function.
Advantages of ASIC Miners
When it comes to the advantages of ASIC miners, their speed and efficiency stand out prominently. These specialized devices can process hashing algorithms at a much faster rate than other mining hardware, which leads to quicker block discovery. Furthermore, their design is tailored specifically for mining, allowing them to consume less power per hash compared to CPUs or GPUs. This not only makes them more energy-efficient but also more cost-effective in the long run. Additionally, the durability of ASIC miners is noteworthy. They tend to have a longer operational life than GPUs that are used for mining, mainly because they are not subjected to the wear and tear that comes from multitasking, as is the case with general-purpose devices.
Criticisms of ASIC Miners
a. Centralization Concerns
The high cost and efficiency of ASICs can lead to mining centralization, where a few entities control a significant portion of the mining power, potentially jeopardizing the decentralized ethos of cryptocurrencies.
b. Lack of Versatility
Unlike GPUs, which can be repurposed for other tasks, ASICs have a singular function. If a particular cryptocurrency changes its mining algorithm or becomes unprofitable, the ASIC designed for it becomes redundant.
c. Environmental Concerns
While ASICs are more energy-efficient than their predecessors, the sheer scale of global ASIC mining operations has raised concerns about their environmental impact.
Popular ASIC Manufacturers

Several companies have emerged as leaders in the ASIC manufacturing space:
- Bitmain: Known for its Antminer series, Bitmain is a dominant player in the ASIC industry.
- MicroBT: Makers of the Whatsminer series, they are significant competitors to Bitmain.
- Canaan Creative: Pioneers in the ASIC space, they produce the AvalonMiner series.
- Ebang: This company offers the Ebit series of ASIC miners with varying performance levels.
The Future of ASIC Mining
With the continuous evolution of the crypto industry, ASICs are also undergoing rapid advancements. The future might see:
- Greater Efficiency: As technology progresses, future ASICs will likely be even more power-efficient.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Innovations might focus on making ASIC mining more sustainable.
- Decentralized Mining Solutions: To address centralization concerns, new ASIC models or mining methods might emerge that democratize access to mining.
Power Infrastructure Essentials
Power infrastructure is the backbone of modern civilization, ensuring that homes, businesses, and industries have the electricity they need to function. As our reliance on technology grows, so does the importance of a robust and reliable power infrastructure. Let’s delve into the intricacies of power infrastructure and its essential components.
What is Power Infrastructure?
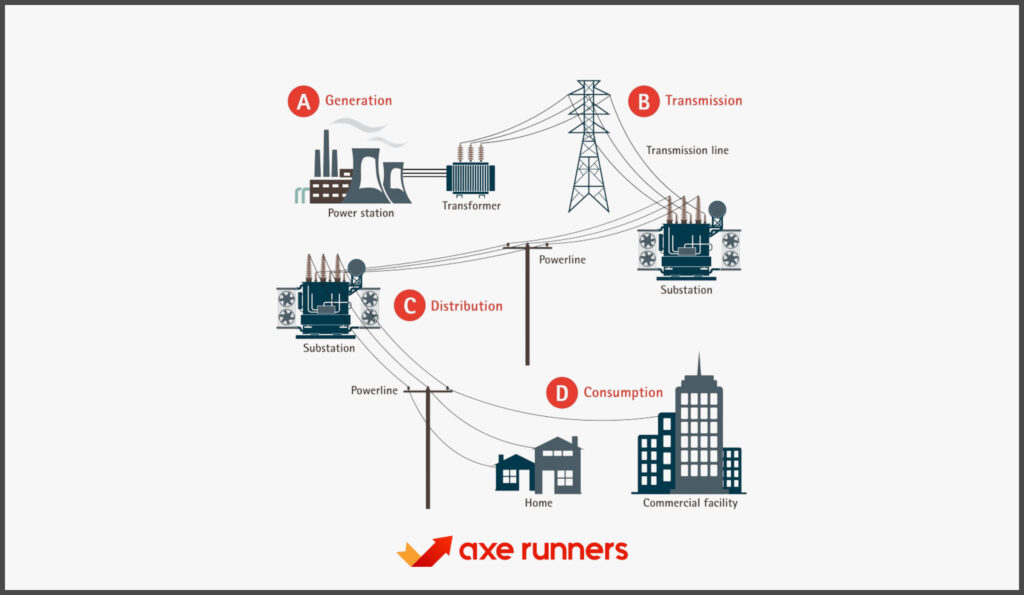
Power infrastructure refers to the interconnected systems and components that generate, transmit, and distribute electricity to end-users. This infrastructure encompasses everything from power plants and substations to transmission lines and distribution networks.
Key Components of Power Infrastructure
a. Generation Facilities
These are the power plants where electricity is produced. They can be:
- Thermal Power Plants: Use coal, natural gas, or oil as fuel.
- Hydroelectric Plants: Harness water flow to generate power.
- Nuclear Power Plants: Use nuclear reactions for electricity generation.
- Renewable Energy Plants: Include solar farms, wind turbines, and geothermal plants.
b. Transmission Systems
Once generated, electricity needs to be transmitted over long distances. This is done using high-voltage transmission lines. Substations along these lines step up or step down the voltage as required.
c. Distribution Networks
These are the lower voltage lines that deliver electricity to homes and businesses. They branch out from substations and cover specific areas or neighborhoods.
d. Substations
Substations play a crucial role in voltage transformation. They can be:
- Transmission Substations: Connect two or more transmission lines.
- Distribution Substations: Connect transmission lines to distribution networks.
Comparison Table: Generation vs. Transmission vs. Distribution
| Criteria | Generation | Transmission | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Produce electricity | Transmit electricity over long distances | Deliver electricity to end-users |
| Voltage Level | Varies based on source | High voltage | Lower voltage |
| Infrastructure | Power plants | High-voltage lines, towers | Lower voltage lines, poles |
Challenges in Power Infrastructure
a. Aging Infrastructure
Many power infrastructures, especially in older cities, are outdated and require significant upgrades to meet current demands.
b. Renewable Integration
As the world shifts towards renewable energy, integrating these sources into the existing grid poses challenges due to their intermittent nature.
c. Security Concerns
With the rise of smart grids and interconnected systems, power infrastructures are becoming more vulnerable to cyberattacks.
d. Environmental and Land Concerns
Building new infrastructure or upgrading existing ones can have environmental impacts and may face opposition from local communities.
The Future of Power Infrastructure
Looking ahead to the future of power infrastructure, several transformative developments are on the horizon. One of the most promising advancements is the emergence of smart grids. These modern grids are equipped with sensors, communication networks, and advanced analytics, all designed to optimize electricity distribution and consumption. As the world continues its shift towards renewable energy sources, the importance of energy storage solutions, such as batteries, becomes even more pronounced.
These storage solutions will play a pivotal role in ensuring a consistent and steady power supply, especially given the intermittent nature of many renewable sources. Additionally, there’s a growing trend towards decentralized power generation. By utilizing microgrids and other decentralized power sources, we can significantly reduce transmission losses and bolster the resilience of our power systems against potential grid failures. This decentralized approach not only enhances efficiency but also empowers communities with more control over their energy sources.
Cooling Systems and Airflow Management
In the modern technological era, cooling systems and airflow management have become paramount, especially in industries like data centers, manufacturing, and even in residential settings. Proper temperature regulation ensures optimal performance, longevity, and safety. Let’s delve deep into the world of cooling systems and understand the significance of efficient airflow management.
Why is Cooling Essential?
Heat is a byproduct of electronic devices, machinery, and various industrial processes. Excessive heat can lead to:
- Reduced efficiency and performance.
- Shortened lifespan of equipment.
- Potential safety hazards.
Types of Cooling Systems
- Passive Cooling
This method relies on natural convection without the use of mechanical devices. It often involves heat sinks, which dissipate heat through materials with high thermal conductivity. - Active Cooling
Active cooling systems use mechanical devices, such as fans or pumps, to circulate air or liquid, effectively dissipating heat. - Liquid Cooling
Liquid cooling systems use a coolant to absorb heat, which is then passed through a radiator and cooled by fans. They are more efficient than air cooling but are typically more complex. - Phase Change Cooling
This advanced method involves changing the physical state of a substance (from liquid to gas) to absorb heat, similar to how air conditioners work.
Comparison Table: Passive vs. Active vs. Liquid vs. Phase Change Cooling
| Criteria | Passive Cooling | Active Cooling | Liquid Cooling | Phase Change Cooling |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Natural convection | Mechanical devices | Coolant circulation | State change of substance |
| Efficiency | Moderate | High | Very High | Extremely High |
| Complexity | Low | Moderate | High | Very High |
| Cost | Low | Moderate to High | High | Very High |
Airflow Management
Airflow management is crucial in environments like data centers, where optimal airflow ensures that hot air is efficiently expelled and cool air is drawn in. Proper airflow management can:
- Reduce energy consumption.
- Prolong equipment life.
- Improve performance.
a. Hot Aisle/Cold Aisle Configuration
This is a common approach in data centers where equipment racks are arranged in alternating rows with cold air intakes facing one way and hot air exhausts facing the other.
b. Containment Systems
These systems physically separate the hot and cold aisles, ensuring minimal mixing of hot and cold air, leading to more efficient cooling.
c. Plenum Spaces
Used in raised floor environments, plenum spaces allow for the distribution of cooled air beneath the floor, which is then drawn up through perforated tiles.
Challenges in Cooling and Airflow Management
As businesses expand and evolve, one of the primary challenges they face is scalability in their cooling systems. The cooling requirements might shift with growth, necessitating solutions that are adaptable and can cater to increased demands. Another significant consideration is energy consumption. Particularly in expansive facilities, cooling systems can be major energy consumers, resulting in substantial operational costs. This energy-intensive nature of cooling not only affects the bottom line but also has broader implications.
Environmental concerns are at the forefront of these implications. Some cooling techniques, notably those that utilize refrigerants, can pose environmental risks if they aren’t handled and managed with care. The potential impact on the environment underscores the importance of choosing and maintaining cooling systems responsibly.
The Future of Cooling and Airflow Management
a. AI and Automation
Advanced algorithms and AI can predict cooling needs and adjust systems in real-time for optimal efficiency.
b. Green Cooling Solutions
With increasing environmental awareness, the focus will shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly cooling solutions.
c. Advanced Materials
The use of materials with superior thermal conductivity, like graphene, can revolutionize passive cooling techniques.
Server Racks and Organization
In the realm of data centers and IT environments, server racks play a pivotal role in ensuring equipment is securely housed, efficiently organized, and optimally cooled. These structures, while seemingly simple, are crucial for the smooth operation of complex technological systems. Let’s delve into the intricacies of server racks and their importance in organizational setups.
What are Server Racks?
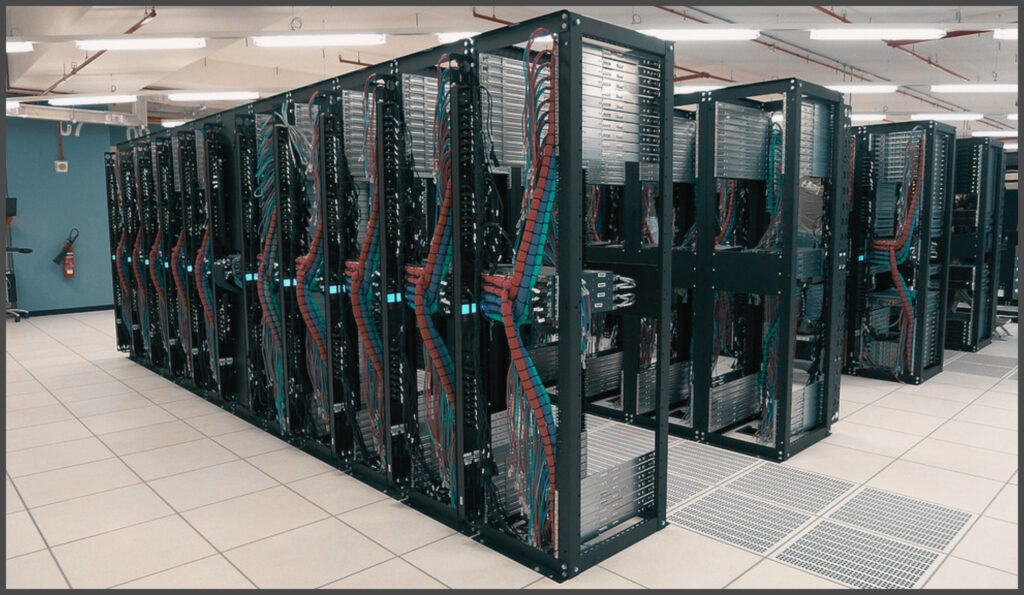

Server racks are standardized frames or enclosures designed to house various IT equipment, including servers, switches, routers, and other related hardware. They provide a centralized location for equipment, facilitating easier management, maintenance, and cooling.
Standard Dimensions
Server racks come in standardized sizes to ensure compatibility with various equipment:
- Rack Units (U)
A rack unit, often denoted as “U,” is a measure of vertical space where 1U is 1.75 inches. Common rack heights include 42U, 48U, and sometimes even 58U. - Rack Width
The standard width for server racks is 19 inches, although there are wider options like 23 inches for specific equipment. - Rack Depth
Depth can vary, with common depths being 600mm, 800mm, and 1000mm, depending on the equipment being housed.
Types of Server Racks
Server racks come in various designs to cater to different needs and environments. Open frame racks, for instance, are essentially just the frame of the rack without any sides or doors. Their open design offers excellent airflow, making them ideal for situations where cooling is a priority. However, this openness means they provide less security for the equipment housed within.
On the other hand, enclosed racks are designed with removable side panels and doors. This design not only offers added security but also allows for better control over the rack’s internal environment, ensuring equipment remains protected from external factors.
Lastly, for locations where floor space is at a premium, wall-mounted racks are the go-to choice. As the name suggests, these racks are designed to be affixed directly to walls, making them perfect for compact environments or when floor-based solutions are impractical. Each of these rack designs serves a unique purpose, ensuring that IT professionals have the flexibility to choose the best fit for their specific needs.
Comparison Table: Open Frame vs. Enclosed vs. Wall-mounted Racks
| Criteria | Open Frame Racks | Enclosed Racks | Wall-mounted Racks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Airflow | Excellent | Good (depends on design) | Moderate |
| Security | Low | High | Moderate to High (depends on design) |
| Space Requirement | Floor space | Floor space | Wall space |
Benefits of Proper Rack Organization
- Efficient Cooling
Organized racks allow for better airflow, ensuring equipment remains at optimal temperatures. - Ease of Maintenance
With well-organized racks, technicians can quickly identify and access equipment, reducing downtime. - Enhanced Security
Organized racks, especially enclosed ones, can prevent unauthorized access to critical equipment. - Space Optimization
Properly organized racks make the most of available space, allowing for more equipment in a given area.
Cable Management in Racks
Cable management is a crucial aspect of rack organization. Properly managed cables lead to:
- Reduced airflow obstructions.
- Easier equipment access and maintenance.
- Reduced risk of cable damage or disconnections.
Future Trends in Server Racks and Organization
- Intelligent Racks
With integrated sensors and IoT capabilities, future racks will provide real-time data on temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors. - Modular Designs
Racks designed to be easily reconfigured will cater to rapidly changing IT environments. - Enhanced Cooling Solutions
As equipment becomes more powerful and generates more heat, racks will incorporate advanced cooling solutions, including liquid cooling.
Security Measures for Mining Operations
Mining operations, whether for precious metals, minerals, or cryptocurrencies, are high-stakes ventures that require robust security measures. The potential for significant financial gains makes these operations prime targets for theft, fraud, and other malicious activities. Let’s delve deep into the security measures essential for safeguarding mining operations.
Understanding the Risks
Before diving into the implementation of security measures for mining operations, it’s imperative to grasp the array of potential threats that loom. One of the primary concerns is physical theft. In the context of traditional mining, this pertains to the illicit removal of mined materials. However, when it comes to cryptocurrency mining, the threat manifests in the form of hardware theft.
Parallelly, digital mining operations are constantly under the shadow of cyberattacks. These digital threats span a range, from ransomware and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks to sophisticated hacking attempts. Beyond the digital realm, there’s the ever-present danger of espionage. Rival entities might be on the prowl for insider information, be it related to lucrative mining locations, proprietary techniques, or mining outcomes.
Additionally, the threat of sabotage cannot be sidelined. Whether stemming from disgruntled employees or competitive adversaries, there’s always a risk of intentional damage to equipment or deliberate disruptions to the mining process. Recognizing these threats is the first step in crafting a robust security strategy.
Physical Security Measures
- Surveillance Systems
Install CCTV cameras at strategic locations to monitor and record activities. - Access Control
Implement biometric systems, keycards, or security codes to restrict unauthorized entry. - Security Personnel
Employ trained security guards to patrol the premises and respond to threats. - Secure Storage
Use safes and secure vaults to store valuable materials or data.
Digital Security Measures (Especially for Cryptocurrency Mining)
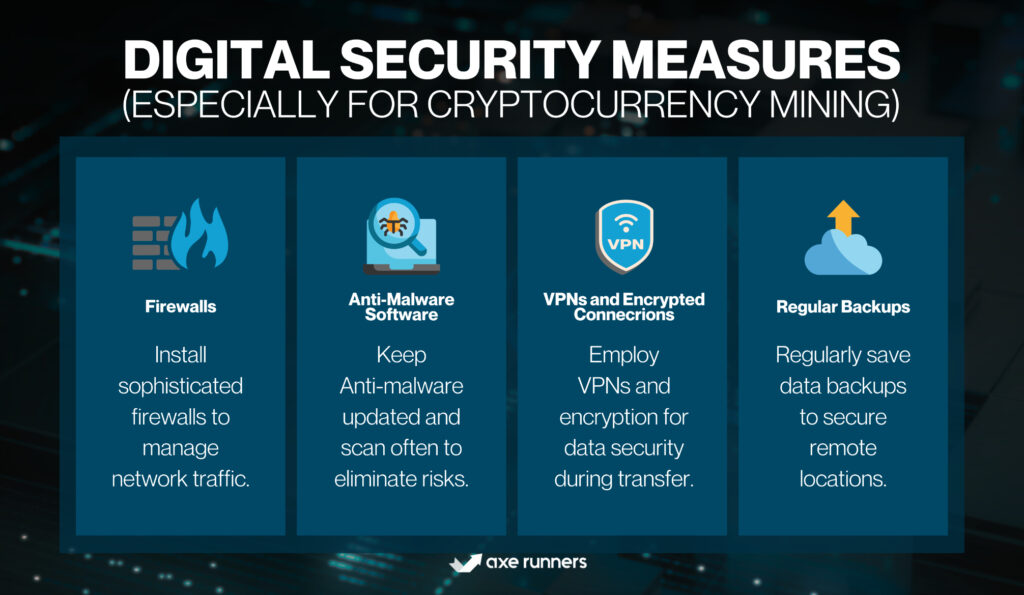
- Firewalls
Deploy advanced firewalls to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. - Anti-Malware Software
Regularly update and run anti-malware tools to detect and remove threats. - VPNs and Encrypted Connections
Use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and encryption to protect data in transit. - Regular Backups
Ensure data is backed up regularly to secure, off-site locations.
Operational Security Measures
One of the cornerstones of a robust security framework is continuous employee training. It’s essential to ensure that staff members are routinely educated on security protocols, emphasizing the critical nature of vigilance in safeguarding assets and data. In tandem with training, implementing two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an additional layer of protection, especially when accessing sensitive systems or data. This dual verification process significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Moreover, to stay ahead of potential threats, it’s prudent to conduct regular security audits. These audits serve as a proactive measure to identify and subsequently rectify any vulnerabilities within the system. However, even with these measures in place, the possibility of unforeseen security breaches remains. Hence, having an incident response plan is paramount. This plan ensures that, in the event of any security lapse or incident, there’s a structured and swift response mechanism ready to be deployed, minimizing potential damage and ensuring timely resolution.
Comparison Table: Physical vs. Digital vs. Operational Security Measures
| Criteria | Physical Security | Digital Security | Operational Security |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Focus | Protecting tangible assets | Protecting digital assets and systems | Ensuring secure daily operations |
| Examples | CCTV, Access Control | Firewalls, VPNs | Employee training, 2FA |
| Implementation | On-site | On servers and computers | Across the organization |
The Future of Security in Mining Operations
- AI and Machine Learning
Advanced algorithms can predict and detect unusual activities, enhancing security measures. - Blockchain for Supply Chain
For traditional mining, blockchain can track and authenticate the origin of minerals, ensuring transparency. - Quantum Cryptography
For digital mining, quantum cryptography can offer next-level security against potential cyber threats.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
In an increasingly interconnected and globalized world, businesses and individuals must navigate a complex web of legal and regulatory considerations. These rules and guidelines, established by governments and international bodies, ensure fair practices, protect rights, and maintain order. Let’s delve deep into the realm of legal and regulatory considerations and understand their significance in various sectors.
Understanding the Basics
- Legislation
Laws enacted by a legislative body, which can be at the local, state, or national level. They provide the framework for rights, duties, and prohibitions in various areas. - Regulation
Rules or directives created by governmental agencies to oversee and control specific industries or activities. They often provide detailed guidelines on how legislation should be implemented. - Compliance
The act of adhering to, and demonstrating adherence to, external laws and regulations, as well as internal policies and procedures.
Key Areas of Legal and Regulatory Considerations
- Business Operations
Licensing: Necessary permissions to operate in certain industries.
Employment Laws: Guidelines on fair treatment, wages, and workplace safety.
Intellectual Property: Protection of patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets. - Financial Sector
Banking Regulations: Rules governing banking operations and customer interactions.
Securities and Exchange: Guidelines on stock market operations and public company disclosures. - Healthcare
Patient Privacy: Laws like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S. protect patient data.
Drug Approvals: Regulations governing the testing and approval of new drugs. - Environment
Emission Standards: Guidelines on permissible levels of pollutants.
Conservation Laws: Rules protecting natural habitats and endangered species.
International Considerations
In the realm of international relations and business, several key legal considerations come to the fore. Trade agreements, for instance, serve as pacts between nations, designed to streamline and facilitate trade. These agreements often focus on reducing tariffs and eliminating other trade barriers, ensuring smoother transactions and fostering economic cooperation.
Parallel to this, in our digital age, data protection and privacy have taken center stage. Notable legislations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, have been enacted to safeguard individuals’ data rights, ensuring that personal information is handled with care and transparency.
Beyond these, the sphere of international business is also governed by stringent anti-corruption laws. Regulations, like the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA), play a pivotal role in curbing bribery and promoting ethical business practices across borders. Together, these legal frameworks shape the contours of global business, ensuring fairness, transparency, and ethical conduct.
Challenges in Navigating Legal and Regulatory Landscapes
- Ever-evolving Nature
Laws and regulations can change frequently, requiring businesses to stay updated. - Jurisdictional Differences
What’s permissible in one country might be illegal in another, complicating operations for multinational entities. - Enforcement Discrepancies
Even with clear regulations, enforcement can vary, leading to uncertainties.
The Future of Legal and Regulatory Considerations
The modern business landscape is undergoing rapid changes, driven by several pivotal factors. At the forefront is digital transformation. As an increasing number of businesses transition to online platforms, there’s a corresponding evolution in the legal framework surrounding e-commerce, digital privacy, and cybersecurity. This shift ensures that both businesses and consumers operate in a secure and transparent digital environment.
Alongside the digital wave, there’s a rising emphasis on sustainable practices. Heightened environmental concerns are prompting stricter regulations centered on sustainability and eco-friendly practices. These regulations aim to ensure that businesses adopt measures that are in harmony with the environment, promoting a greener future.
Additionally, in our interconnected world, global collaboration is becoming the norm rather than the exception. Such international cooperation is likely to pave the way for more standardized regulations, fostering a sense of uniformity and mutual understanding across borders. Together, these trends highlight the dynamic nature of the business world and the adaptive legal frameworks that support it.
Conclusion
In today’s fast-paced world, marked by technological advancements and global collaboration, adaptability and foresight are paramount. As industries evolve with digital shifts and sustainability becomes a core focus, staying agile and informed is essential.
The increasing interconnectedness of nations underscores the importance of ethical conduct and shared responsibility. Embracing change and fostering collaborative efforts will be key to navigating the promising yet uncertain future that lies ahead.
At axerunners.com, our goal is to furnish well-rounded and trustworthy information regarding cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and stocks. Nonetheless, we avoid providing financial advice and instead encourage users to conduct their own research and meticulous verification.
Read More













+ There are no comments
Add yours